pYSFReflector
This is a YSF Reflector implemented in python3, mainly compatible with g4klx reflector.
Additional Features
Enhanced Blocking List
With the enhanced blocking list you are able to mute calls based on
- callsign of sender
- callsign of gateway used
- ip-address of gateway
This rules only mute traffic from the gateway to the reflector. For gateways and ip-adresses of gateways are additional rules for bi-directional blocking implemented which could be used to stop delivering traffic to a specific gateway (for example on multinet-setups to have a network insulated for a specific time because of special conditions or stoping traffic to guys sniffing traffic and transporting it into systems that are unwanted - 'wild bridges' for example).
Blocking On Regular Expression Callsign Check
It is also possible to use (by default enabled in the YSFReflector.ini) a callsign check based on a regular expression to check the callsign plausibility in callsign-format and length.
The result of this check can be overdriven by a whitelist-entry in the blocklist (for example: N0CALL is blocked by default by this expression but could be allowed for special bridging situations).
Muting Matrix
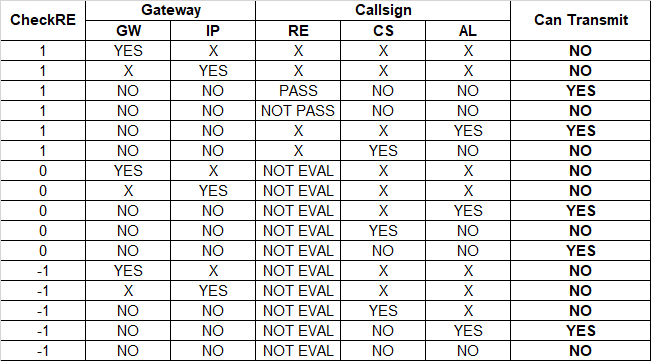
Here you see a matrix documenting the behavior of the blocking-lists and configuration of regular expression (RE)-check:
Within this table following descriptions for the cell-values should help understanding the table:
- X: Any value
- YES: set and matches with callsign/gateway/ip-address
- NO: not set
- 1: check via RE enabled, normal operation
- 0: check via RE disabled, but passes everything
- -1: check via RE disabled, but only pass whitelist
Avoiding Parallel Incomming Transmissions
There is also a functionality implemented that prohibits parallel transmissions that can happen if two senders transmit at the same time. Here the principle 'first-comes-first-serves' is realized, so the second station in time will just be muted to not disturb the audio.
Easy Installation And Upgrade
Depending on your used operating system and python3-installation you just have to take care that following libraries are installed:
- bisect
- configparser
- datetime
- os
- queue
- re
- signal
- socket
- struct
- sys
- threading
- time
In most installations this packages are already installed, otherwise you easily can install them with your system-package-manager (for example Debian: apt) or you use pip3 install -command.
The configuration file (YSFReflector.ini) is based on the origin YSFReflector.ini of G4KLX's YSFReflector but with added new configuration-items. So If you know the old reflector-software - configuring this one would be straight forward.
Best Practise Installation
For getting the best user experience it is recommended to configure your pYSFReflector with the following parameter in the YSFReflector.ini:
FileRotate=0
This results in having only one logfile for each program and having it rotated by your linux-system with logrotate if configured.
If you are using the php-based Dashbord by DG9VH (https://github.com/dg9vh/YSFReflector-Dashboard) please leave it at FileRotate=1, if you are using the websockets based version (recommended at https://github.com/dg9vh/WSYSFDash) you can use FileRotate=0. Take care to configure the dashboard's logtailer.ini in sync to this.
To configure log rotation in Linux take a look at https://www.tecmint.com/install-logrotate-to-manage-log-rotation-in-linux/.
Setting FileLevel in Logging
actually the FileLevel-Logging is done in 3 variant loglevels: 0 to 2. Here is a short description what is logged in the different levels:
- Level 2: Only messages on startup and error-messages are logged
- Level 1: All from level 2 plus normal messages created when running the reflector. This level is recommended if you are running a dashboard with the reflector.
- Level 0: All from level 1 and 2 plus some additional information about remote-commands not needed in regular situations. This level shows the full log.