NFM modulator plugin
Introduction
This plugin can be used to generate a narrowband frequency modulated signal. "Narrowband" means that the bandwidth can vary from 1 to 40 kHz.
Interface
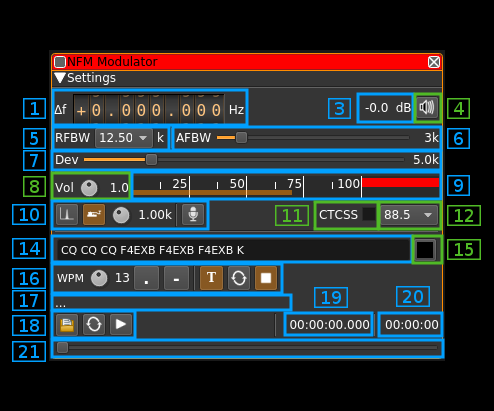
1: Frequency shift from center frequency of transmission
Use the wheels to adjust the frequency shift in Hz from the center frequency of transmission. Left click on a digit sets the cursor position at this digit. Right click on a digit sets all digits on the right to zero. This effectively floors value at the digit position. Wheels are moved with the mousewheel while pointing at the wheel or by selecting the wheel with the left mouse click and using the keyboard arrows. Pressing shift simultaneously moves digit by 5 and pressing control moves it by 2.
3: Channel power
Average total power in dB relative to a +/- 1.0 amplitude signal generated in the pass band.
4: Channel mute
Use this button to toggle mute for this channel.
5: RF bandwidth
This is the bandwidth in kHz of the channel signal filtered after modulation. It can be set in discrete values: 3, 4, 5, 6.25, 8.33, 10, 12.5, 15, 20, 25 and 40 kHz
6: Audio frequency bandwidth
This is the bandwidth in khz of the modulating signal filtered before modulation. It can be set in kHz steps from 1 to 20 kHz
7: Frequency deviation
Adjusts the frequency deviation in 0.1 kHz steps from 0 to 25 kHz
8: Volume
This is the volume of the audio signal from 0.0 (mute) to 2.0 (maximum). It can be varied continuously in 0.1 steps using the dial button.
9: Level meter in %
- top bar (beige): average value
- bottom bar (brown): instantaneous peak value
- tip vertical bar (bright red): peak hold value
You should aim at keeping the peak value below 100% using the volume control
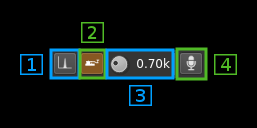
10: Input source control
10.1: Tone input select
Switches to the tone input. You must switch it off to make other inputs available.
10.2: Morse keyer input select
Switches to the Morse keyer input. You must switch it off to make other inputs available.
10.3: Tone frequency (kHz)
Adjusts the tone frequency from 0.1 to 2.5 kHz in 0.01 kHz steps
10.4: Audio input select and select audio input device
Left click to switch to the audio input. You must switch it off to make other inputs available.
Right click to select audio input device. See audio management documentation for details.
11: CTCSS switch
Checkbox to switch on the CTCSS sub-audio tone
12: CTSS tone frequency
Select the CTCSS sub-audio tone in Hz among these values: 67.0, 71.9, 74.4, 77.0, 79.7, 82.5, 85.4, 88.5, 91.5, 94.8, 97.4, 100.0, 103.5, 107.2, 110.9, 114.8, 118.8, 123.0, 127.3, 131.8, 136.5, 141.3, 146.2, 151.4, 156.7, 162.2, 167.9, 173.8, 179.9, 186.2, 192.8 and 203.5 Hz
14: CW (Morse) text
Enter the text to be keyed when Morse input is active and in text mode
15: Clear CW text
Clears the CW (Morse) text
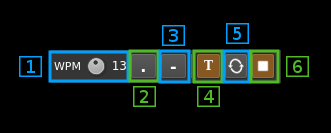
16: Morse keyer controls
16.1: CW keying speed
Sets the CW speed in Words Per Minute (WPM). This is based on the word "PARIS" sent 5 times. For 5 WPM the dot length is 240 ms. In other terms the dot length is calculated as 1.2 / WPM seconds. The dot length is used as the base to compute other timings:
- Element (dot or dash) silence separator: 1 dot length
- Dash: 3 dot lengths
- Character silence separator: 3 dot lengths
- Word silence separator: 7 dot lengths
16.2: Dots keying
Switch this button to send dots continuously
16.3: Dashes keying
Switch this button to send dashes continuously
16.4: Text keying
Switch this button to send the text typed into the text box (14)
16.5: Text auto repeat
Switch this button to auto repeat the text keying
12.6: Text play/stop
Use this button to stop sending text. When resuming keying restarts at the start of text
⚠ WARNING: what follows is not really useful if you do not use a proper Morse keyer with direct audio feedback. There is a significant audio delay either with the direct monitoring or by monitoring the transmitted signal so keying with this audio as feedback is not practical
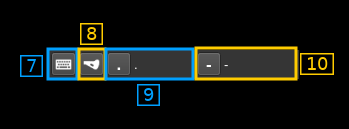
12.7: Activate morse keys keyboard control
This disables text or continuous dots or dashes. Toggle input from keyboard. Occasionnaly the focus may get lost and you will have to deactivate and reactivate it to recover the key bindings.
12.8: Iambic or straight
Choose iambic or straight keying style. When straight is selected the dot or dash key may be used.
12.9: Register dot key
Click on the button and while selected type a character or character and modifier (Shift + key for example) to select which key is used for dots. The key or key sequence appears next (here dot .)
12.10: Register dash key
Click on the button and while selected type a character or character and modifier (Shift + key for example) to select which key is used for dashes. The key or key sequence appears next (here dot .)
17: Audio file path
The path to the selected audio file to be played or dots if unselected
18: Audio file play controls
18.1: Audio file select
Opens a file dialog to select the audio file to be played. It must be mono 48 kHz F32LE raw format. Using sox a .wav file can be converted with this command: sox piano.wav -t raw -r 48k -c 1 -b 32 -L -e float piano.raw
18.2: Audio file loop
Audio replay file at the end
18.3: Play/pause file play
Toggle play/pause file play. When paused the slider below (17) can be used to randomly set the position in the file when re-starting.
19: Play file current position
This is the current audio file play position in time units relative to the start
20: Play file length
This is the audio file play length in time units
21: Play file position slider
This slider can be used to randomly set the current position in the file when file play is in pause state (button 18.3)