Add sizeToContents in ChannelGUI and FeatureGUI, called when widget is rolled, so we can remove resizing code from all of the individual channels and features. In RollupContents, use minimumSizeHint for calculated size, so that minimumWidth can come from .ui file. In DeviceGUI::sizeToContents(), call adjustSize(), so Device GUIs start out at minimum needed size (which should restore appearance prior to last patch). In stackSubWindows, use available space for channels if no spectrum/features present. In stackSubWindows, fix spectrum from being sized too big, resulting in scroll bars appearing. Reset user-defined channel width in stackSubWindows, when channels are removed. Don't stack maximized windows. There's one hack in Channel/FeatureGUI::maximizeWindow(). It seems that when maximimzing a window, QOpenGLWidgets aren't always paint properly immediately afterwards, so the code forces an additional update. I can't see why the first call to paintGL doesn't work.
Remote sink channel plugin
Introduction
This plugin sends I/Q samples from the baseband via UDP to a distant network end point. It can use FEC protection to prevent possible data loss inherent to UDP protocol.
Build
The plugin will be built only if the CM256cc library is installed in your system. For CM256cc library you will have to specify the include and library paths on the cmake command line. Say if you install cm256cc in /opt/install/cm256cc you will have to add -DCM256CC_DIR=/opt/install/cm256cc to the cmake commands.
Interface
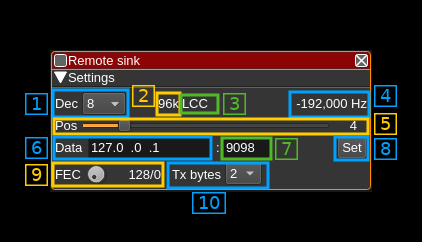
The top and bottom bars of the channel window are described here
1: Decimation factor
The device baseband can be decimated in the channel and its center can be selected with (5). The resulting sample rate of the I/Q stream sent over the network is the baseband sample rate divided by this value. The value is displayed in (2).
2: Network I/Q stream sample rate
This is the sample rate in kS/s of the I/Q stream sent over the network.
3: Half-band filters chain sequence
This string represents the sequence of half-band filters used in the decimation from device baseband to resulting I/Q stream. Each character represents a filter type:
- L: lower half-band
- H: higher half-band
- C: centered
4: Center frequency shift
This is the shift of the channel center frequency from the device center frequency. Its value is driven by the device sample rate , the decimation (1) and the filter chain sequence (5).
5: Half-band filter chain sequence
The slider moves the channel center frequency roughly from the lower to the higher frequency in the device baseband. The number on the right represents the filter sequence as the decimal value of a base 3 number. Each base 3 digit represents the filter type and its sequence from MSB to LSB in the filter chain:
- 0: lower half-band
- 1: centered
- 2: higher half-band
6: Distant address
IP address of the distant network interface from where the I/Q samples are sent via UDP
7: Data distant port
Distant port to which the I/Q samples are sent via UDP
8: Validation button
When the return key is hit within the address (1) or port (2) the changes are effective immediately. You can also use this button to set again these values.
9: Desired number of FEC blocks per frame
This sets the number of FEC blocks per frame. A frame consists of 128 data blocks (1 meta data block followed by 127 I/Q data blocks) and a variable number of FEC blocks used to protect the UDP transmission with a Cauchy MDS block erasure correction. The two numbers next are the total number of blocks and the number of FEC blocks separated by a slash (/).
10: Transmission sample size
Number of bytes per I or Q sample in transmission.