2.7 KiB
Audio input plugin
Introduction
This input sample source plugin gets its samples from an audio device.
Interface
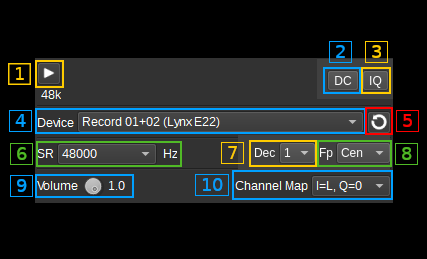
The top and bottom bars of the device window are described here
1: Start/Stop
Device start / stop button.
- Blue triangle icon: device is ready and can be started
- Green square icon: device is running and can be stopped
- Magenta (or pink) square icon: an error occurred. In the case the device was accidentally disconnected you may click on the icon, plug back in and start again.
2: Auto remove DC component
Software DSP auto remove DC correction. This will work in I/Q mode (stereo I/Q) only.
3: Auto make I/Q balance
Software DSP auto I/Q imbalance correction. The DC correction (8) must be enabled for this to be effective. This will work in I/Q mode (stereo I/Q) only.
4: Device
The audio device to use.
5: Refresh devices
Refresh the list of audio devices.
6: Audio sample rate
Audio sample rate in Hz (Sa/s).
7: Decimation
A decimation factor to apply to the audio data. The baseband sample rate will be the audio sample, divided by this decimation factor.
8: Decimated bandpass center frequency position relative the device center frequency
This will work in I/Q mode (stereo I/Q) only.
- Cen: the decimation operation takes place around the device center frequency Fs
- Inf: the decimation operation takes place around Fs - Fc.
- Sup: the decimation operation takes place around Fs + Fc.
9: Volume
A control to set the input volume. This is not supported by all input audio devices.
10: Channel Map
This controls how the left and right audio channels map on to the IQ channels.
- Mono L - Real samples are taken from the left audio channel and are heterodyned by the fourth of the sample rate (fs/4) to obtain complex samples. Therefore the spectrum of the complex baseband is centered at the fourth of the sample rate (fs/4). As per Nyquist rule only a bandwidth of half of the sample rate (fs/2) is available for real signals. Frequencies outside the [0, fs/2] interval are artefacts and can be eliminated by decimating by a factor of 2.
- Mono R - Same as above but takes the right audio channel for the real signal.
- I=L, Q=R - The left audio channel is driven to the I channel. The right audio channel is driven to the Q channel for a complex (analytic signal)input.
- I=R, Q=L - The right audio channel is driven to the I channel. The left audio channel is driven to the Q channel for a complex (analytic signal)input.